Energy measurement
According to FIESC, electrical energy waste in Brazil is estimated at 43 terawatt-hours (TWh) per year, which is equivalent to serving 20 million homes. This waste is mainly caused by the lack of maintenance and the long period of use of engines in the industrial sector.
According to the National Electric Energy Agency (ANEEL), 55% of energy production in Brazil comes from water sources. As much as it is a renewable source, a hydroelectric plant changes the ecosystem where it is installed.
With population growth, energy production is increasingly necessary. This project aims to identify this waste of energy, allowing the end consumer to use their energy intelligently and consequently reducing the need for unnecessary use of natural resources.
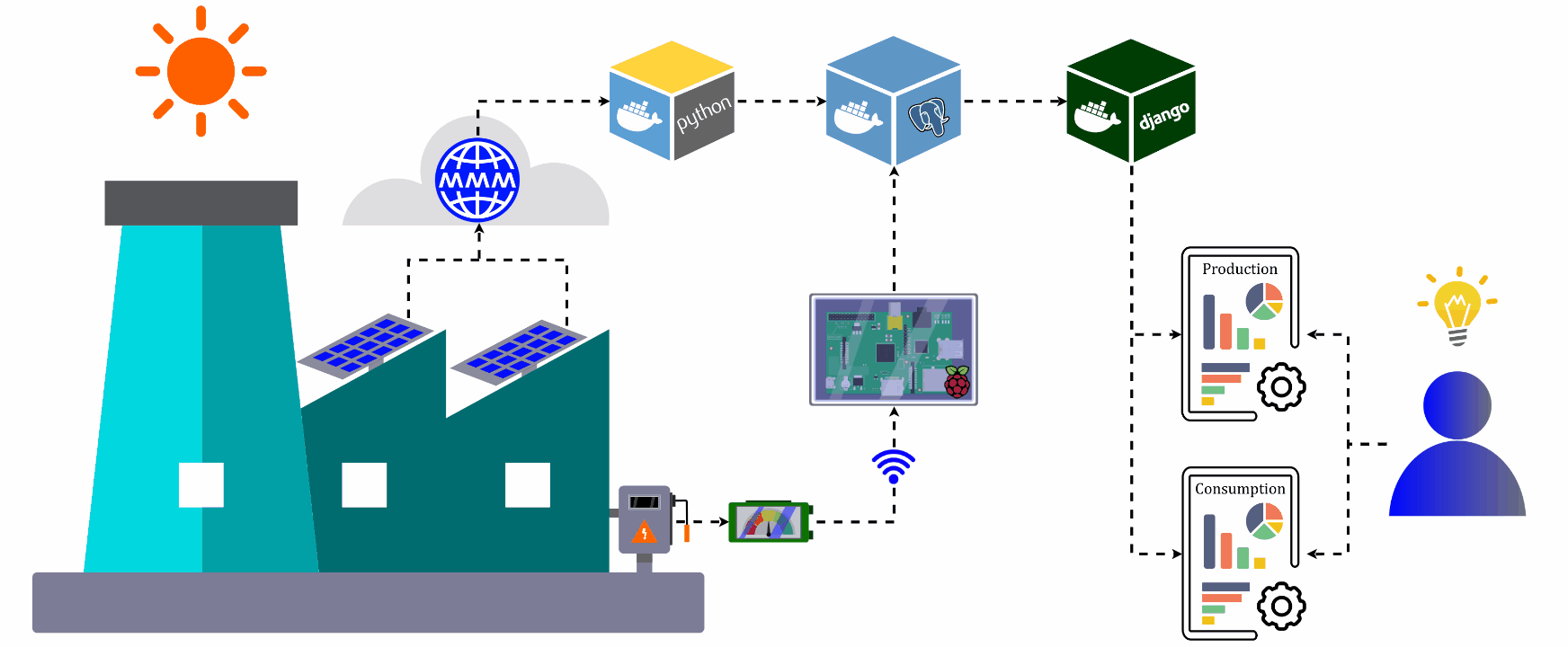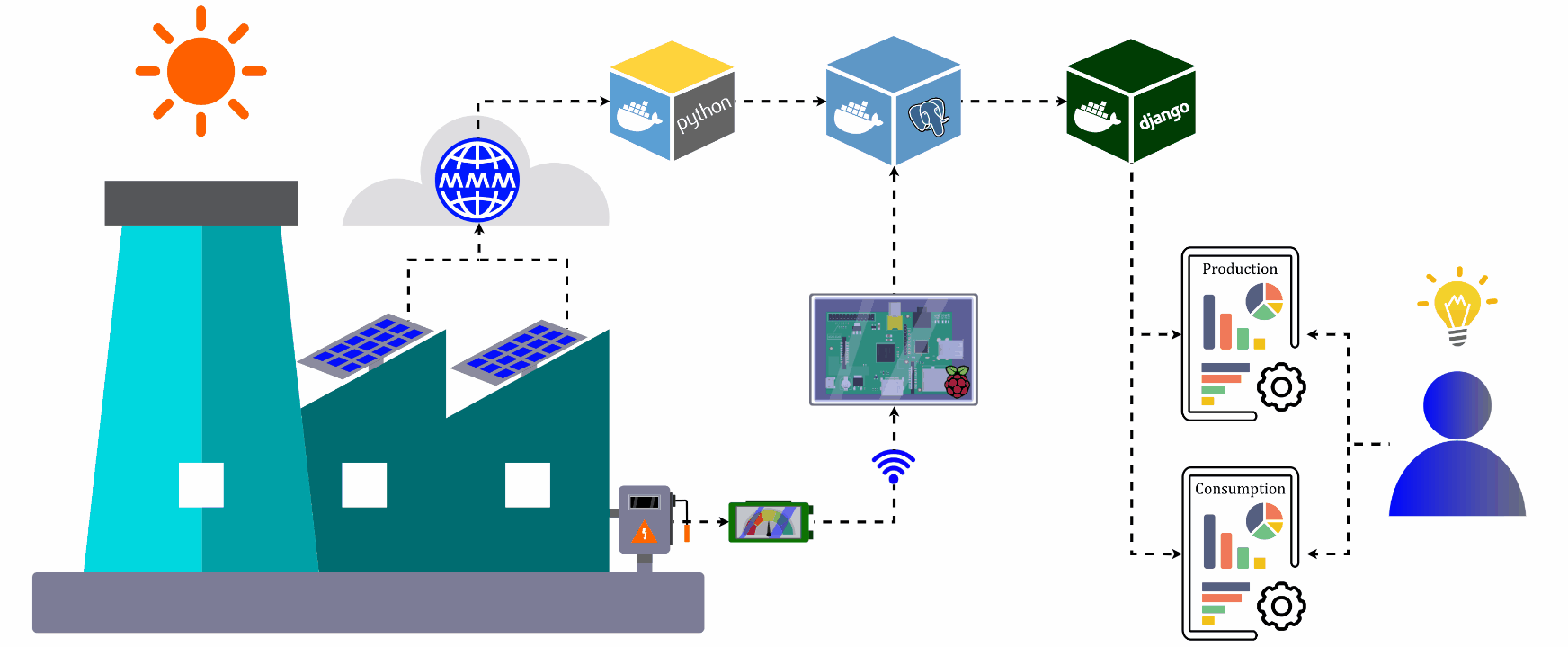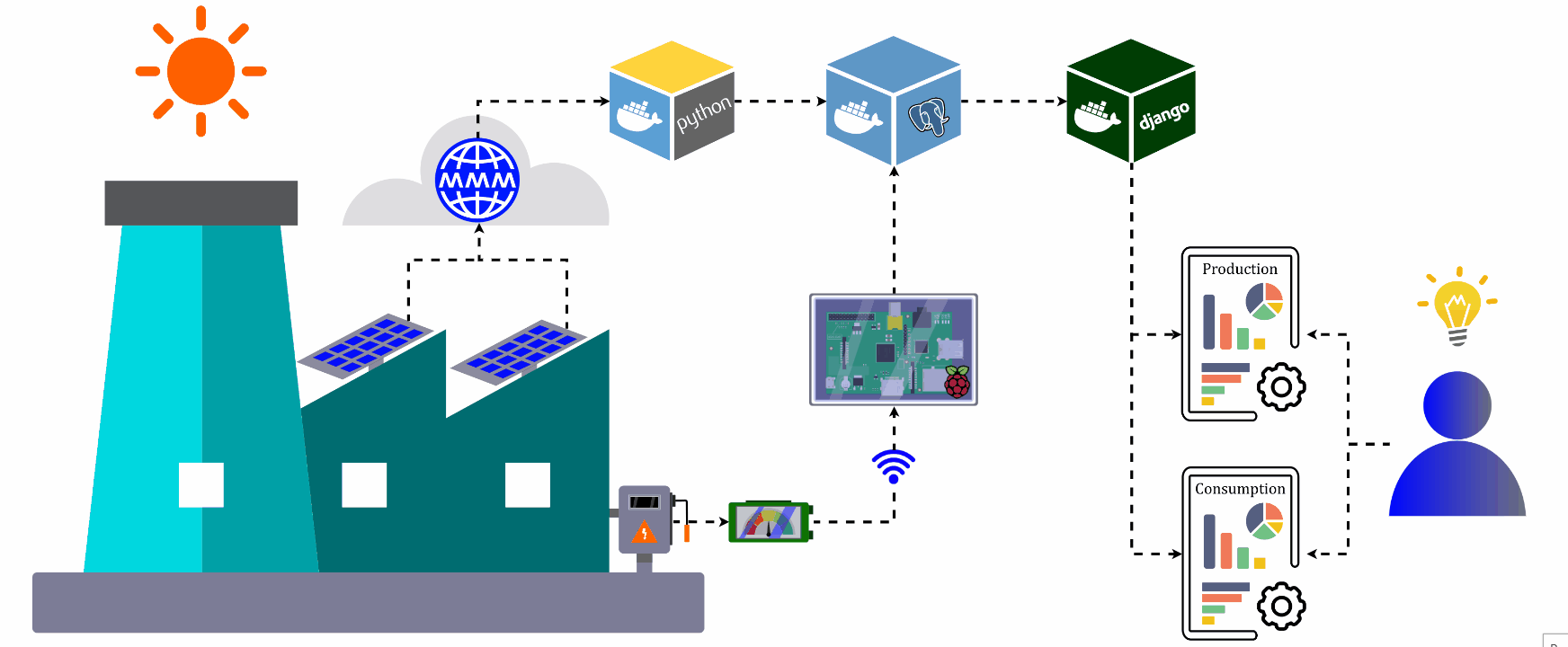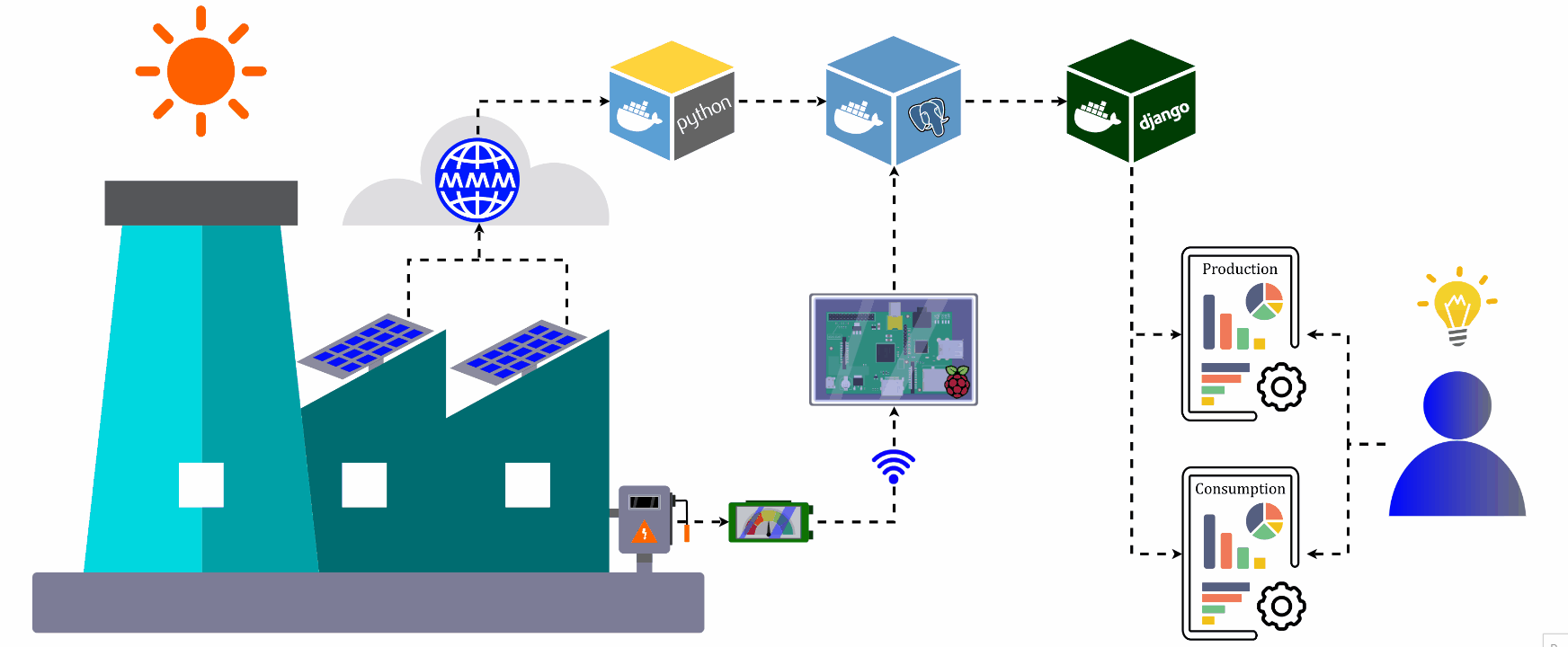
This project measures energy production through the analysis of photovoltaic modules and consumption through active power analysis directly at the central distribution board. The photovoltaic module sends the data to a server in the cloud and through a Python API this data is queried and stored in the database. To collect data from the central distribution board, commercial devices are used that use a Wi-Fi signal to send the data to a center that formats the data and sends it to the database. After the data arrives in the database, reports are generated in a user interface that assists and directs the user in decision making.
Software and technologies used:
Ubuntu: Operational system.
Docker: Containerize applications.
Database: PostgreSQL.
Central: Raspberry pi to receive data, format and send to database.
Meter: Commercial meter to measure active power and send the data to central using Wi-Fi.
Django: User interface.
Want to know more about
Don't hesitate to get in touch
It will be a pleasure to speak with you
